
Designing Effective Layouts for AI Interfaces
As artificial intelligence continues to reshape the digital landscape, the interfaces we build for interacting with it must evolve too. Whether it’s a chatbot, a recommendation engine, a visual AI tool, or an intelligent assistant, the layout of an AI-powered interface can significantly impact usability, trust, and engagement. Whether it’s an AI interface or non-AI interface, the design needs to be accessible, understandable, and aligned with user goals.
The key principles and layout strategies for designing intuitive and effective AI interfaces are
1. Prioritize Clarity and Transparency
AI systems often operate as black boxes, making it essential for the interface to explain what the AI is doing. This doesn’t mean revealing every algorithmic detail, but the layout should include:
- Status Indicators: Show when the AI is “thinking” or “listening.”
- Output Context: Display how results were generated.
- User Guidance: Offer hints or examples of what users can say, ask, or input.
Google’s AI-powered search results now include “About this result” panels that explain why a page was recommended—adding transparency to the algorithm.
2. Modular and Flexible Grids
AI interfaces often display dynamic content: changing predictions, real-time suggestions, or evolving conversation threads. Layouts should be modular to adapt to this.
- Use responsive grid systems that can reflow content as needed.
- Design modular components (cards, chat bubbles, panels) that can be reordered or resized depending on input/output.
A visual search AI might have a split-screen layout, with one side for the query image and the other showing results in an adjustable grid.
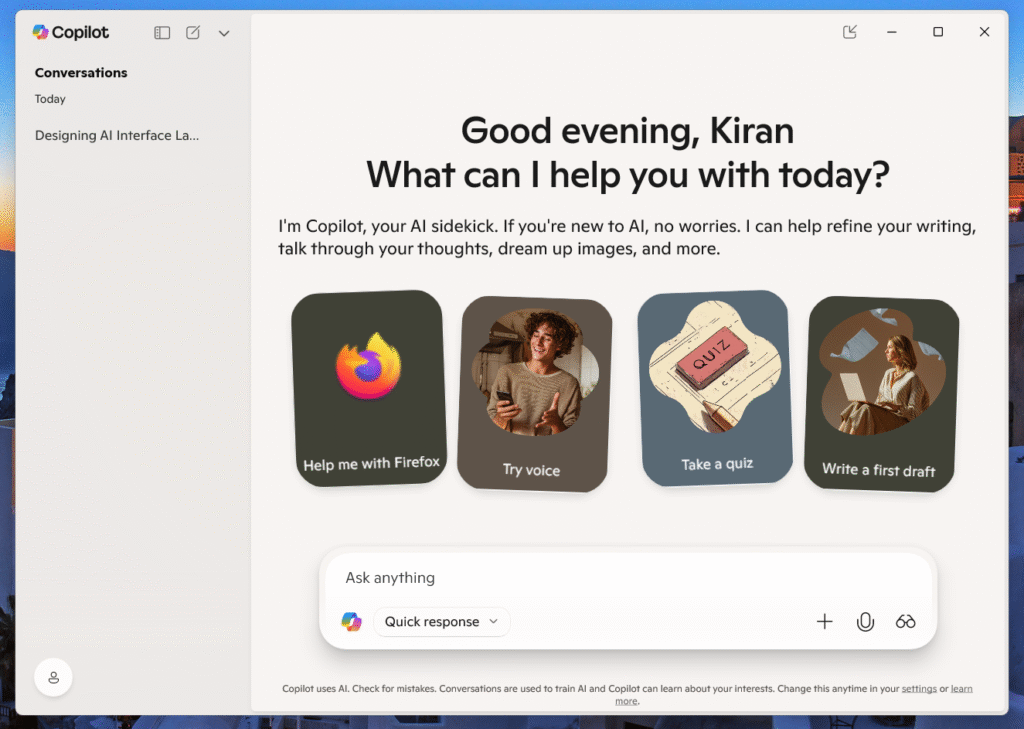
3. Conversational Interfaces Need Structure
Chat-based or voice interfaces are common with AI—but they need more than just a textbox and a feed of messages.
Design should include:
- Context Pointers: Summarize recent interactions or goals at the top of the screen.
- Turn Separation: Visually differentiate user inputs from AI responses (e.g., alignment, color, icons).
- Suggested Actions: Add quick-reply buttons, filters, or feedback controls under each message.
Pro Tip: Anchor these suggestions contextually within the conversation rather than placing them in a static footer.
4. Human-AI Collaboration Zones
Interfaces that involve co-creation (e.g., design tools, code assistants, content generators) need space for both the human and AI to “work.”
Layout Ideas:
- Split-pane interfaces: One pane shows the user’s canvas/code, the other the AI’s suggestions.
- Timeline layouts: Display iterative improvements or versions, allowing users to compare or revert.
- Action areas: Use floating toolbars or modals to surface AI tools without overwhelming the screen.
5. Feedback and Control Mechanisms
Users must be able to guide, correct, or fine-tune the AI. The layout should encourage this through:
- Inline Feedback: Let users thumbs-up/down specific outputs or mark them as irrelevant.
- Adjustable Settings: Offer sliders or toggles for tone, speed, level of creativity, etc.
- Undo/Redo Zones: Prominently display undo options in areas where AI can make major changes.
Design Note: Keep control elements close to the AI-generated content—proximity reduces friction.
Grammarly’s interface allows users to accept, reject, or modify AI suggestions—giving them full control over the final output.
6. Mobile-First Considerations
Many AI experiences, especially voice assistants and chatbots, are mobile-first. On smaller screens:
- Use collapsible menus for advanced options.
- Prioritize vertical stacking for AI output and controls.
- Ensure input areas are always accessible and not obstructed by the keyboard.
7. Aesthetics and Emotion
AI interfaces benefit from visual warmth—users are often wary of overly robotic or sterile designs. Use:
- Friendly microcopy: Humanized text helps users feel at ease.
- Visual cues: Animation or avatars can humanize responses without being gimmicky.
- Soft color palettes: Avoid high-contrast, mechanical themes unless it fits the product’s branding.
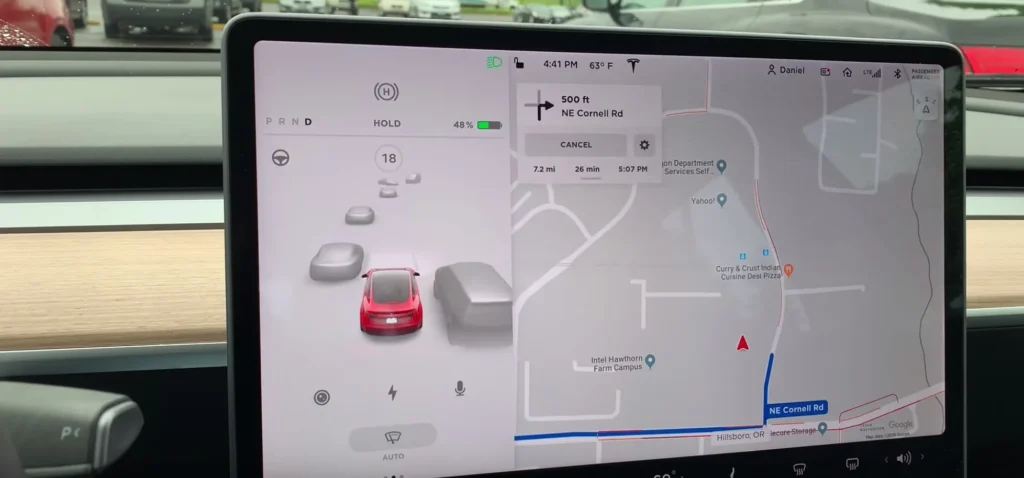
Tesla’s autopilot interface uses bold visual cues to show detected objects, lane boundaries, and system status—ensuring drivers know what the AI sees.
The best AI interface layouts aren’t just beautiful – they’re thoughtful, transparent, and empowering. Designing effective layouts for AI interfaces is both an art and a science. It requires empathy for users, a deep understanding of AI behavior, and a commitment to clarity. As AI continues to evolve, so too must our design strategies ensuring that these powerful tools remain accessible, trustworthy, and human-centered. By embracing modularity, clarity, and user control, designers can create interfaces that make AI feel less like a machine and more like a helpful partner.



